Difference between revisions of "HFE"
From Genetics Wiki
(→Protein Sequence) |
(→Protein Sequence) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
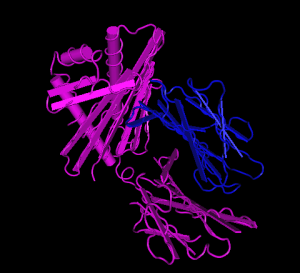
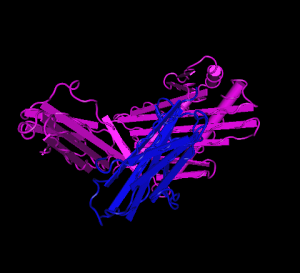
''HFE'' tertiary complex with ''beta2M'' | ''HFE'' tertiary complex with ''beta2M'' | ||
| − | [[File:HFE-beta2M.png|300px]] | + | [[File:HFE-beta2M.png|300px]][[File:HFE-beta2M-2.png|300px]] |
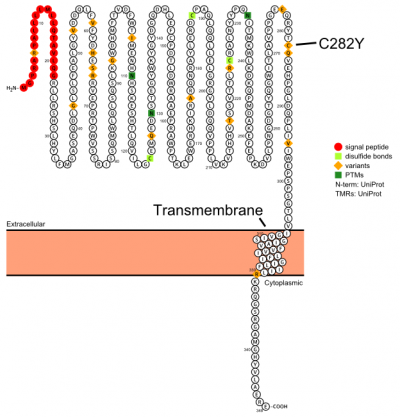
Plot in Protter[http://wlab.ethz.ch/protter/] with UniProt accession: Q30201 | Plot in Protter[http://wlab.ethz.ch/protter/] with UniProt accession: Q30201 | ||
[[File:HFE protter.png|400px]] | [[File:HFE protter.png|400px]] | ||
Revision as of 09:39, 18 July 2014
HFE is named after High Fe (iron). The gene products known function is to regulate iron absorption by interacting with transferrin and its receptor. When the normal function is disrupted by mutation the result can be HFE hereditary hemochromatosis or iron overload.
DNA Sequence
HFE is located on chromosome 6 in humans.
RNA Sequence
There are several alternatively spliced variants of HFE.
Protein Sequence
The protein has a signal sequence and transmembrane domain. It forms a tertiary complex with beta2-microglobulin (beta2M). HFE has sequence and structural similarity to MHC class I-type proteins.
NCBI Protein[1]
>gi|4504377|ref|NP_000401.1| hereditary hemochromatosis protein isoform 1 precursor [Homo sapiens] MGPRARPALLLLMLLQTAVLQGRLLRSHSLHYLFMGASEQDLGLSLFEALGYVDDQLFVFYDHESRRVEP RTPWVSSRISSQMWLQLSQSLKGWDHMFTVDFWTIMENHNHSKESHTLQVILGCEMQEDNSTEGYWKYGY DGQDHLEFCPDTLDWRAAEPRAWPTKLEWERHKIRARQNRAYLERDCPAQLQQLLELGRGVLDQQVPPLV KVTHHVTSSVTTLRCRALNYYPQNITMKWLKDKQPMDAKEFEPKDVLPNGDGTYQGWITLAVPPGEEQRY TCQVEHPGLDQPLIVIWEPSPSGTLVIGVISGIAVFVVILFIGILFIILRKRQGSRGAMGHYVLAERE
NCBI Structure[2]
HFE tertiary complex with beta2M
Plot in Protter[3] with UniProt accession: Q30201