Cohen-Boyer-Berg experiment
In 1973 the first living genetically engineered transgenic organism was made in the Cohen-Boyer-Berg experiment.
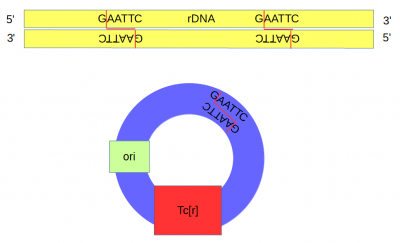
A plasmid (pSC101[1]) containing a gene conferring resistance to tetracycline (Tcr) and an origin of replication was cut at a single site with the restriction enzyme EcoRI.
DNA from an African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) was also cut with EcoRI and this yielded a range of DNA fragments including a large number of ribosomal DNA (that codes for rRNA) fragments[2] with matching "sticky ends".
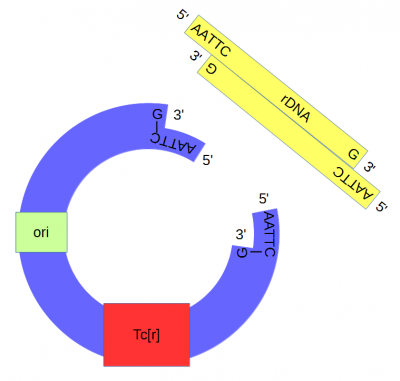
The cut plasmid and Xenopus DNA were mixed together with a ligase to repair the cut site, incorporating the Xenopus rRNA fragment into a fraction of the plasmids.
A population of E. coli cells were then transformed to incorporate the plasmids into their cells and grown on media containing tetracycline to select for the cells that contained the plasmid conferring tetracycline resistance. These could then be screened to identify the cells with plasmids that had incorporated the Xenopus DNA.
The end result was a bacteria that stably replicated a fragment of amphibian ribosomal DNA.